Old and Modern Heap Exploit Technique : Unlink Exploit
Understanding how unlinking happens in libc (old and modern) and how to exploit it
Unlink Exploit
In this blog I will try to explain the historical unlink heap exploit technique and also show examples of how it works. I have had a hard time understanding how this technique works, so i thought let me try to explain it to someone else (via this blog post at least) to see if i really understood the technique.
Overview
These technique is triggered by the unlink macro hence the name. The unlink macro is used to remove a free chunks from the middle of a bin (double-linked list), the bins include unsorted bin, small bin, and large bin. The tcache/fastbin are singly-linked-lists they won’t apply the unlink mechanism . This exploit has a write-what-where primitive .
To clearly understand this technique we first have to understand heap consolidation.
Heap Consolidation.
When a chunk is remove from a bin, the unlink() macro is called on the chunk. The unlink macro looks like this:
1
2
3
4
5
FD = P->fd; /* forward chunk */
BK = P->bk; /* backward chunk */
FD->bk = BK; /* update forward chunk's bk pointer */
BK->fd = FD; /* updated backward chunk's fd pointer */
At first this macro was difficult for me to understand so here is another way to view it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
/*
Curr = current chunk (P)
Next = next chunk in doubly linked list (FD)
Prev = previous chunk in doubly linked list (BK)
*/
Next = Curr->fd;
Prev = Curr->bk;
Next->bk = Prev;
Prev->fd = Next;
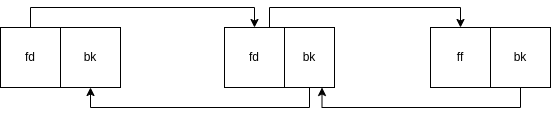
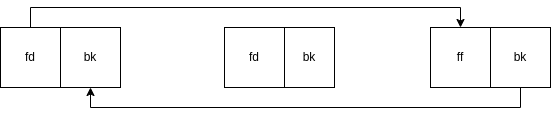
The macro is changing the pointers of the chunks before (BK/Prev) and after (FD/Next) the victim chunk (P/Curr). The below images show how the macro works in the unlink process.
The middle chunk is being unlinked.
Before Unlink
After Unlink
In older glibc versions we can use this vulnerability to modify the fd and bk pointers of the P/Curr chunk to perform arbitrary read/write primitive after the macro executes. This is called the unsafe unlink.